What are lipomas?
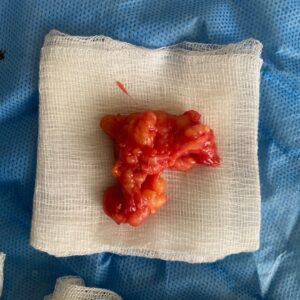
Lipoma is the most common benign soft-tissue tumor. It is basically an accumulation of immature fat cells. They are commonly found in subcutaneous fatty tissue. They feel soft and generally do not cause pain. Rarely, lipomas can cause constriction of nerves and may hurt.
Lipomas can usually be easily identified by ultrasound. In the case of close proximity to nerves or vessels as well as atypical examination findings, a scan is helpful. A malignant change is very rarely possible. Evidence of this can be found in rapid growth or pain. Malignant liposarcomas tend to affect patients between the ages of 50 and 65.
What are the most common benign tumors of soft tissue?
- Sebaceous Cyst: It is a cavity filled with yellowish-white toothpaste-like material in the subcutaneous tissue. It is caused by a disorder of the sebaceous glands. If it increases in size or if there is a risk of inflammation, it can be surgically removed.
- Lipomas: A lipoma is a benign proliferation of fatty tissue cells. In rare cases, however, the growth can be malignant. Only surgical removal can confirm the diagnosis.
How is a Lipoma removed?
Most lipoma excision or removal at Contura Clinic is performed under local anesthesia. Occasionally in people who have multiple lipomas general or spinal anesthesia may be needed depending on your needs. There are two options for local anesthesia: Either the skin in the surgical area is anesthetized or the surgeon specifically anesthetizes the nerve that supplies the surgical area.
Most Lipomas are removed via incisions that are less than 1/3rd their diameter. The scar is well hidden and minimized as much as possible. It takes around 2-5mins to remove each lipoma
Liposuction for lipoma is another treatment option. This is especially useful for large lipomas. But there is a slight chance of recurrence of lipomas following liposuction as sometimes the thin capsule around the lipoma or some fat cells may be left behind.